Promoting a Sustainable Future through Bee-Friendly Gardening: Unlocking the Benefits
This post may contain affiliate links which might earn us money. Please read my Disclosure and Privacy policies hereBees are essential for pollination, supporting biodiversity and food production, but their populations are declining due to habitat loss, pesticides, and climate change.
Promoting bee-friendly gardening can help sustain these vital pollinators and enhance ecological health. This article provides practical tips for creating gardens that support bees and boost biodiversity.
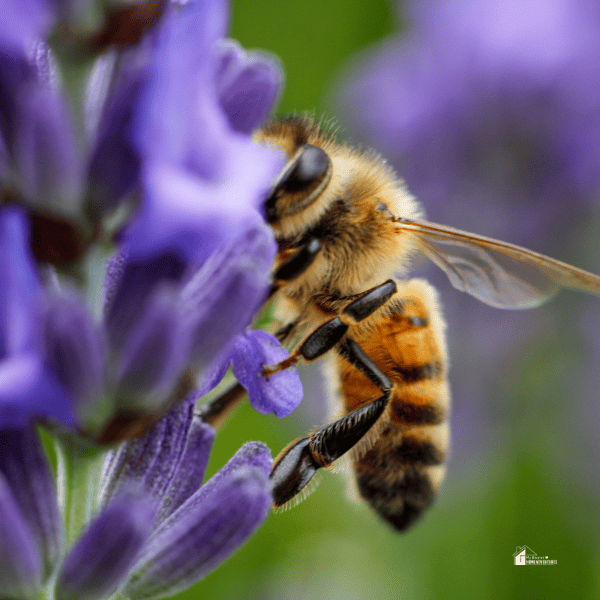

The Vital Role of Bees in Our Environment
Bees are an integral part of ecosystems, playing a critical role in pollination that supports biodiversity, food production, and ecological balance. Just as bees contribute to the environment, human actions, like adopting renewable energy sources, can have a direct positive impact on ecological health. Utilizing solar power for a home is one such action, reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing our carbon footprint, which helps combat climate change—a major factor affecting bee populations.
Beekeepers often rely on tools like a bee hive insulation cover to protect their colonies during colder months. This ensures that bees can survive the winter and continue their pollination work in spring, which is vital to maintaining ecosystem health.
As pollinators, bees support the reproduction of countless flowering plants, promoting biodiversity while ensuring the production of food staples like fruits, seeds, and nuts. Let’s explore the importance of bees further:
Pollination Services
Bees pollinate about 75% of the world's flowering plants and approximately 35% of global food crops. They are responsible for critical crops such as apples, almonds, blueberries, and cucumbers. Without bees, agricultural productivity would suffer, impacting food security worldwide.
Biodiversity Support
By pollinating a wide variety of plants, bees help maintain genetic diversity within plant populations, which is crucial for plant survival in the face of diseases, pests, and environmental changes.
Bees also promote the growth of trees, flowers, and plants that provide habitats and food for diverse wildlife species, reinforcing their role in a broader ecosystem.
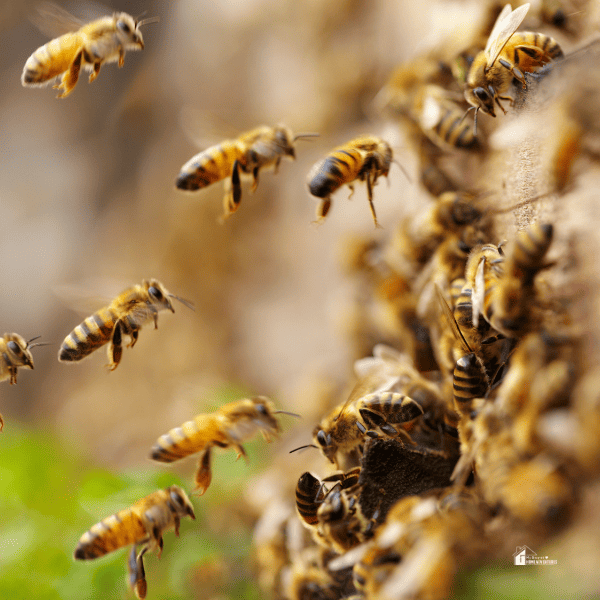

Ecosystem Stability
In addition to supporting biodiversity, bees contribute to ecosystem stability by promoting healthy plant populations. They are vital in maintaining soil structure, preventing erosion, and enhancing nutrient cycling.
Bees also indirectly support water quality, as the plants they pollinate assist in filtering water and regulating water flow—another form of ecosystem service that benefits human populations.
Economic Impact
With bees leading the charge, animal pollination boosts global crop yields by an estimated $235 to $577 billion annually. Their work ensures the continued production of fruits, nuts, and other essential crops that anchor the world’s food supply.
Beekeeping is also a thriving industry that supports economic growth in rural and urban areas, provides employment and boosts local economies.
How to Build a Bee-Friendly Garden
Designing a bee-friendly garden requires thoughtful planning to ensure bees can access the habitat and resources they need. Follow these steps to create an inviting garden for these essential pollinators:
Choosing the Ideal Location
- Sunlight: Choose a sunny spot, as bees thrive in warm environments. Place the garden near a water source to help bees stay hydrated.
- Avoid Chemicals: To protect bees from harmful chemicals, keep your garden away from pesticide-treated zones. Choose low-traffic spots to avoid disturbing their activities.
Selecting Bee-Friendly Plants
- Diverse Plant Variety: Opt for a range of flowering plants that bloom in different seasons, ensuring bees have a continuous food supply from spring through fall. Try always to have at least two plant types blooming simultaneously.
- Native Species: Include native flowers and plants, such as lavender, borage, sunflowers, or herbs like thyme and basil, which are particularly attractive to local bee species.
- Cluster Planting: Group flowers together rather than spreading them out, making food sources easier for bees to locate.
- Flower Diversity: Offer a mix of shapes and colors to appeal to various bee species. Some prefer open, shallow blooms, while others are attracted to tubular flowers.
Providing Nesting and Hydration Sources
- Nesting Materials: Certain bees, such as leafcutter bees, need specific materials for nest building. Plant shrubs or trees that can supply these resources.
- Bee Hotels: Provide safe nesting sites by setting up bee hotels in a sunny location to accommodate solitary bees.
- Water Source: Install a shallow water feature topped with stones or small corks so bees can safely land and drink. Refresh the water regularly to prevent stagnation and mosquito breeding.
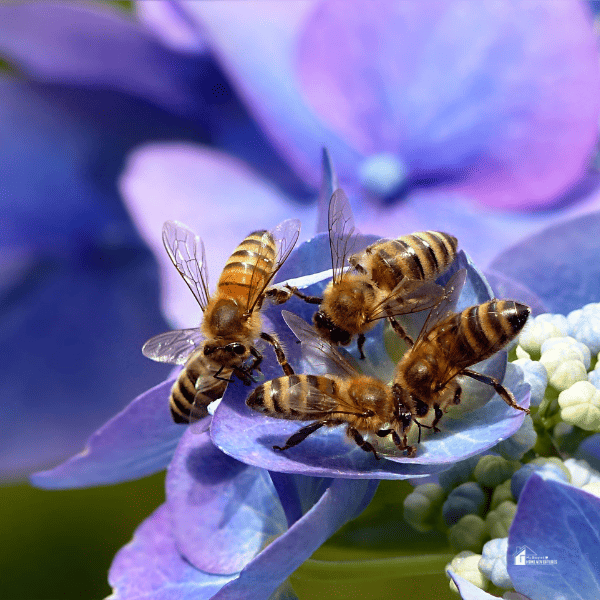

Garden Maintenance and Care
- Limited Weeding: Allow certain wild plants like clovers and dandelions to grow, offering bees extra pollination resources.
- Chemical-Free Practices: Avoid using herbicides and pesticides. If necessary, select low-toxicity products and apply them when bees are less active, such as early morning or late evening.
| Expert Tips: Allow herbs, vegetables, and other plants to go to seed before trimming them back to extend the food source for bees. |
How to Safely Handle a Bee Swarm in Your Garden
If you find a bee swarm in your garden, follow these active steps to manage the situation safely:
Identify the Swarm
Quickly confirm it's a swarm of honey bees, not wasps or other stinging insects. Honey bees have fuzzy bodies with black and yellow stripes. Observe from a safe distance, noting the swarm's size—typically about the size of a basketball.
Avoid Disturbing the Swarm
Please resist the urge to spray the bees with water or chemicals, as this only aggravates them. Keep children and pets away, and avoid loud noises or throwing anything at the swarm to prevent stressing the bees.
Contact a Beekeeper
Immediately call a local beekeeper or bee removal expert to relocate the swarm safely. Provide essential details like the swarm's location, size, and accessibility. If possible, send a photo to help them prepare properly.
Wait for the Beekeeper
If the swarm isn't in a problematic spot, leave it alone and wait for the bees to move on, which often happens within a day or two. If they are easily accessible, the beekeeper may relocate them without charge.
| Leave Remove to the Experts: Avoid any attempts to remove the swarm yourself unless you're an experienced beekeeper. Spraying pesticides or trying to smoke them out will backfire, often forcing the bees deeper into your property. Sealing their entry point also risks trapping them inside, leading to further complications |

Bee-Friendly Gardening: A Path to a Thriving Ecosystem
Promoting a sustainable future through bee-friendly gardening is crucial for preserving biodiversity and protecting ecosystem health.
Individuals can significantly impact bee conservation by recognizing the importance of bees, implementing bee-friendly practices, and supporting local beekeepers.
Leveraging available resources and staying informed on best practices will strengthen these efforts, driving us toward a more resilient and sustainable environment.